Tinnitus & Ayurved - Cause, Diagnosis, Treatment
18.11.2009 | What Is Tinnitus? Many people experience hearing loss as they grow older, but auditory nerve damage from noise can affect anyone, no matter what their age. From middle age and beyond, up to 30 percent of the American population is estimated to begin suffering from a ringing in their ears. Called Tinnitus, this condition is estimated to affect up to 50 million Americans.
Ayurveda College “Vishwa Shanti Dham”, Wagholi, Tal. Haveli, Pune, India on the occasion of the performance of a lecture in the “Yoga in Daily Life” - Centre on
Friday 12th June 2009 in Vienna, Austria.
Tinnitus affects most sufferers temporarily, often immediately after exposure to loud noise, like after attending a rock concert. That muffled hearing with an underlying hum or buzz is tinnitus. Fortunately for most of us, the hearing loss and noise passes in a few hours or minutes, but for many tinnitus sufferers it is a way of life.
Some people suffering from tinnitus say they hear a noise in the background all the time, but only if they listen for it. However, other sufferers report hearing incessant humming, chirping, clicking, rustling and a variety of other noises all of the time.
For some people tinnitus can be simply an annoyance. For those suffering the most severe symptoms, the condition can lead to chronic sleeplessness, depression and even thoughts of suicide.
Loud noise exposure is just one of a wide range of health and environmental issues that cause tinnitus. One of the biggest misconceptions about tinnitus is that nothing can be done about it. The lack of hope that their condition can ever improve often worsens not only the outlook, but the symptoms, of the tinnitus sufferer.
The reality is that most causes of tinnitus CAN be treated. The key is determining where in the hearing process the tinnitus is coming from, or if it stems from an underlying medical problem. Although in some cases this is impossible, it helps to determine what treatments might be the most effective.
We hope that this e-book and CD series will help those plagued by these bothersome, sometimes debilitating. By finding the right medical professionals and conjuring up the ability to change some habits, the vast majority of tinnitus patients can experience significant relief.
Some of the most effective treatments can be as simple as making some lifestyle changes. Others require medication, homeopathic treatment, hearing aids or surgery. The key to finding relief for tinnitus is often related to finding a medical professional capable of ruling out issues that could be causing the symptoms to pinpoint an effective treatment.
If you are like the majority of people, you do not have to simply learn to live with tinnitus, whether you find it simply annoying or incredibly maddening. We hope this series will help you find the treatment that works for you.
The Hearing Process
It helps to be informed about how we hear to understand why tinnitus is often so difficult to pinpoint and treat. The breakdown can occur anywhere in the auditory pathway.
We hear because of a complicated series of events that allows the ear to convert sound waves into electrical signals and to send nerve impulses to the brain to be interpreted as sound.
The ear is made up of three areas: the outer, middle, and inner ear. Sound waves enter through the outer ear and travel to the middle ear where they cause the ear drum to vibrate. The vibrations are transmitted through three tiny bones in the middle ear called the ossicles. These three bones are commonly known as the hammer, anvil and stirrup. In medicine, they are called the malleus, incus, and stapes.
The ear drum and ossicles carry the vibrations to the inner ear. The stirrup transmits the vibrations through the oval window and into the fluid that fills the inner ear. The vibrations move through fluid in the snail-shaped hearing part of the inner ear, which is called the cochlea. The cochlea also contains hair cells. The fluid in the cochlea moves the top of the hair cells, which causes the production of nerve impulses.
The nerve impulses produced in the inner ear are carried to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. Different sounds stimulate different parts of the inner ear, allowing the brain to distinguish among various sounds, for example, different vowel and consonant sounds.
Tinnitus can be caused be a problem in the middle ear, the inner ear, the auditory nerve or even in the brain. The problem may not be in the head at all – tinnitus may be caused by a general health problem like a low thyroid level or high blood pressure.
It's important to find a health practitioner who is willing to take the time to at least rule out some of the many causes of tinnitus to help you find a solution to decrease or end the constant noise. That positive reassurance is key to recovering from tinnitus.
What Causes Tinnitus?
One of the most frustrating aspects of tinnitus is that it can be caused by a host of things ranging from age and environment to general health to hearing loss.
One physician describes a patient with very bothersome tinnitus who actually had a hair rubbing against his ear drum that caused the problem. The noise immediately went away completely once the hair was removed from the ear canal.
There are so many different factors, conditions and triggers for subjective tinnitus that many times physicians can't pinpoint a specific cause even after exhaustive examination and testing. However, here are some of the more likely causes:
Exposure to loud noise. Loud music, engines, equipments, music and gunfire can lead to noise-induced tinnitus as well as hearing loss.
Age-related hearing loss. Becoming hard of hearing also results in tinnitus. Because many people lose hearing as they age, tinnitus is more common in older people. Age-related hearing loss usually begins around age 60.
Medication. The American Tinnitus Association states that more than 200 medications can cause or contribute to tinnitus. It's important to rule out medication as a factor. Some drugs are toxic to the ear while others produce tinnitus as a side affect. Be sure to tell your doctor if you are taking aspirin or any medication with aspirin or a high-dose diuretic. Some intravenous antibiotics also can damage the ear. Medication-induced tinnitus may be temporary or permanent.
General health problems. Problems with the neck, jaw and head cause tinnitus. So can heart and vascular problems, allergies and tumors.
Earwax buildup. Sometimes a buildup of wax in the ear canal can cause tinnitus. It should be removed by a medical professional.
Infections. Both sinus and ear infections can cause tinnitus. Often the disturbance will go away once the infection is cured.
TMJ and other jaw problems. Jaw muscle spasms can cause problems that cause a noise of jaw joints or muscles.
Fibromyalgia. This debilitating, chronic inflammation of the muscles, tendons and ligaments frequently includes TMJ, which often includes tinnitus as a symptom.
Head and neck trauma. After a concussion or other head or neck injury, patients can experience tinnitus and dizziness.
Inner ear problems. Sometimes structures in the inner ear are diseased or malformed. Other times something as simple as the hairs inside the inner ear become broken and cause the auditory cells to report electrical impulses to your brain as sound.
Ear infection. An undiagnosed ear infection can cause tinnitus.
Blood vessel problems. With age, sometimes the blood vessels close to the ear lose elasticity. This causes blood flow to be more forceful. The result can sometimes be pulsatile tinnitus. Malformed capillaries, which are tiny blood vessels, sometimes cause tinnitus as well.
Lyme Disease. This tick-borne disease has been known to cause tinnitus in some patients.
Who Gets Tinnitus?
Most tinnitus occurs as part of the aging process, often over the age of 60. People who suffer head trauma, specific birth defects and diseases can also suffer from the condition.
Anybody of any age who suffers from hearing loss tends to experience tinnitus.
Children who have the condition often are less bothered by it than adults because they have often experienced the constant noise, along with the hearing loss, their entire lives.
Anyone can develop tinnitus if they are exposed to loud noises. Although one or two incidences are not as likely to be harmful, hearing sensitivity varies widely from person to person.
Prolonged exposure to loud noises at either work or play can put you at risk. Medication that poisons ear, and problems with ear structures can cause hearing loss and tinnitus.
Although researchers haven't determined whether tinnitus is hereditary, they have discovered that some of the conditions that have tinnitus as symptoms may have a genetic predisposition. They include some forms of rare kinds of hearing loss, TMJ, Ménière's disease and a benign tumor in the ear called acoustic neuroma.
Tinnitus Symptoms
According to the American Tinnitus Association (ATA), at least 12 million Americans hear an ongoing or frequent ringing, roaring, clicking or hissing sound in their ears.
Some estimates say that perhaps one in five people have some degree of tinnitus and that 30 percent of the population will suffer from it at least once in their lifetime.
ATA estimates that at least 1 million tinnitus sufferers experience the symptoms to a point that it interferes with their daily activities. People with severe cases of tinnitus often find it difficult to hear, work or sleep. They describe the symptoms of ringing or chirping in their ears as incessant, loud and distracting.
The word "tinnitus" comes from Latin and means "to tinkle or to ring like a bell." It is generally pronounced "tin NITE us" in the United States, but "TIN it us" is an acceptable pronunciation as well. The condition is divided into two types – objective and subjective. Objective tinnitus is the less common form of the disorder.
Diagnosing Tinnitus
In addition to getting a very detailed medical history to rule out other health factors, medical professionals can run several simple tests to determine hearing loss often associated with tinnitus.
The tonal quality of tinnitus is often important in rendering a potential cause as well as a treatment plan. Lower-toned noises are often associated with Ménière's disease, one of the most common causes of subjective tinnitus. High-pitched tinnitus is more common in people with either high-frequency hearing loss or hearing loss associated with middle ear problems.
It is important for the physician to determine whether the hearing loss associated with your tinnitus is related to nerve damage or some other problem. They can do that by figuring out what kind of hearing loss you have. There are three different types of hearing loss, conductive, sensor neural and mixed.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is not conducted properly through the outer ear, the eardrum and the ossciles, the bones of the middle ear. It usually involves a reduction in sound level, or the ability to hear faint sounds. Conductive hearing loss can often be medically or surgically corrected. In some cases the tinnitus will decrease with treatment.
Conditions that cause conductive hearing loss can include anything from allergies and earwax to a foreign body or tumor. Most causes of objective tinnitus also can cause this type of hearing loss.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensor neural hearing loss happens when there is damage to the inner ear or to the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. This type of hearing loss cannot be medically or surgically corrected. It is a permanent. The tinnitus associated with it, however, may be treated.
This type of hearing loss not only involves a reduction in sound level, or the ability to hear faint sounds, but also affects understanding speech and the ability to hear clearly.
Sensor neural hearing loss can be caused by diseases, injury during the birth process, drugs that are toxic to the auditory system, and genetic factors. It may also occur as a result of noise exposure, viruses, head trauma, aging and tumors.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Sometimes a conductive hearing loss occurs in combination with a sensor neural hearing loss. In this case, there may be damage to the middle ear as well as the inner ear or auditory nerve. Depending on the circumstances, hearing loss and tinnitus may be improved with treatment.
If sound appears to come from the side that the patient perceives the unilateral hearing loss, the hearing loss is conductive. If the sound appears to occur on the side away from the side of unilateral hearing loss, it is sensor neural.
By using several types of hearing tests, medical practitioners can further characterize hearing loss as being sensory, arising from the inner ear, or neural, arising from the auditory nerve. Narrowing down where the hearing process breaks down can help you and your health care provider find a treatment or cure that will work for the ringing in your ears.
If your physician believes you have objective tinnitus, you may be sent for further testing. Most doctors order an examination and some imaging, either an MRI or an MR Angiogram, which is an MRI with a specific blood vessel study. Sometimes they'll also order a CAT scan, which looks at bony architecture, and sometimes you ever have to proceed with an arteriogram of the blood vessels and the brain blood vessels in skull.
Tinnitus Treatment
If you have objective tinnitus, you are lucky. Most likely you can be successfully treated. The treatment can be as a simple as removing wax from your ear, or in the case of pulsate tinnitus, surgically removing a malformed blood vessel or embolism.
Subjective tinnitus is virtually always more difficult to treat. Part of the reason treatment is so challenging is because it takes some commitment on the medical professional's part to conduct a wide range of tests and a thorough personal history to at least narrow down, if not definitely discover, where the problem arises in the hearing process.
Another reason tinnitus sufferers get insufficient treatment is because a lot of the responsibility falls on them. They may be required to change their diet to avoid trigger foods or live a healthier lifestyle to help them overcome physical conditions that have caused tinnitus.
Most medical professionals say there's a significant psychological component to tinnitus treatment as well. Especially in severe cases, where tinnitus sufferers are depressed and experiencing high anxiety and sleeplessness, a positive attitude can make a huge difference.
It's important that the medical professional who you choose to treat your tinnitus knows that their support and your outlook is important.
Tinnitus treatment options and Tinnitus relief:
• Tinnitus Masker (Masking)
• Tinnitus Retraining Therapy
• Electrical Stimulation Therapy for Tinnitus
• Where to Find a Knowledgeable Tinnitus Physician
• Alternative Treatment For Tinnitus
• Tinnitus Cure
• Homeopathic Treatment for Tinnitus
• Treating Tinnitus With Nutritional Supplements
• Medication For Tinnitus | Tinnitus Drug Therapy
• Psychological Treatment for Tinnitus
• Hearing Aids For Treating Tinnitus
What is too loud?
Damage occurs to the inner ear after people experience one single, extremely loud noise, like a gunshot close to their ear, or a loud noise over a long period of time. It's a combination of both threshold and duration.
Just one 140-decibel noise for a second is very injurious. A 100-decibel noise for a second is not injurious, but over a period of several hours, days, weeks, months or years it is.
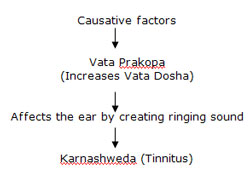
According to Ayurvedic point of view
Causative factors:
a) Shrama (Excessive physical stress)
b) Kshaya (Malnutrition, weakness)
c) Ruksha Bhojana (Excessive dry diet)
d) Kashaya Bhojana (Excessive astringent taste diet)
e) Viriktashirashya sheetasevana ( Consumption of cold things after medicated nasal drops)
f) Sheeta Rutu ( Cold Climate)
Symptoms:
Specific sound like “Venughosha” means sound which generates due to wind through Bamboo Shoot.
Etiology:
Treatment :-
1) Ghrutapana: Consumption of Medicated Ghee.
2) Rasayana (Rejuvenation): Cow’s milk + Cow’s Ghee
3) Karnapoorana (explained later): Medicated ear drops.
4) Snehavirechana: Purgation with the help of medicated ghee.
Things to be avoided:
1) Excessive talking.
2) Head bath.
3) Excessive Exercise
4) Excessive sexual intercourse.
AYURVEDA ACADEMY of YOGA IN DAILY LIFE
Montigasse 13, A-1170 Vienna, Austria
Tel/Fax: +43-1-485 37 02
mob. +43 676 391 00 07
info@AyurvedaAcademy.org
www.AyurvedaAcademy.org
.jpg)


.png)




